Citation
Abstract
Purpose
To propose new methods for eye selection in presbyopic monovision corrections.
Methods
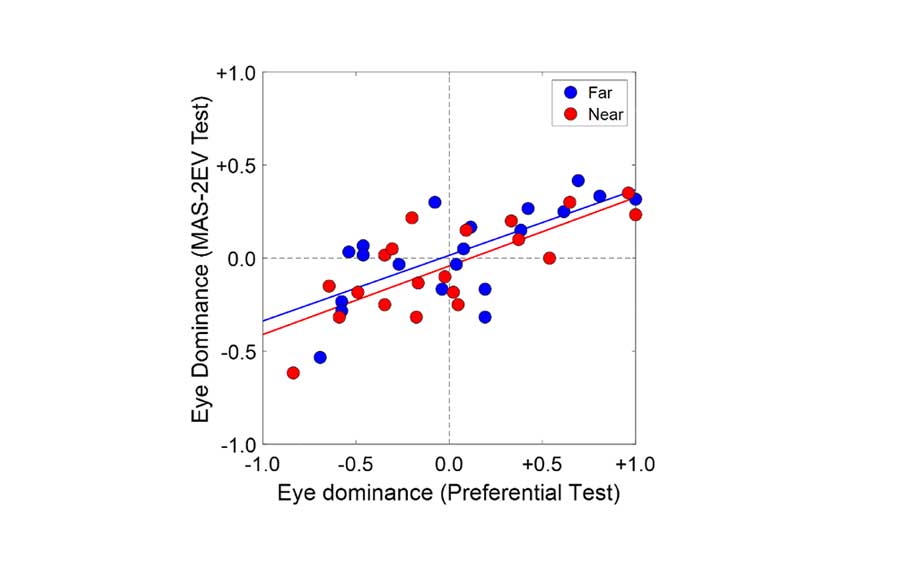
Twenty subjects with presbyopia performed two standard methods of binary eye dominance identification (sensory with +1.50 diopters [D ]and +0.50 D and sighting with “hole-in-the-card”) and two psychophysical methods of perceived visual quality: (1) the Preferential test, 26 natural images were judged with the near addition in one eye or in the other in a 2-interval forced-choice task, and the Eye Dominance Strength (EDS) defined as the proportion of trials where one monovision is preferred over the other; (2) the Multifocal Acceptance Score (MAS-2EV) test, the perceived quality of a natural images set (for 2 luminance levels and distances) was scored and EDS defined as the score difference between monovision in one eye or the other. Left-eye and right-eye dominance are indicated with negative and positive values, respectively. Tests were performed using a Simultaneous Vision Simulator, which allows rapid changes between corrections.
Results
Standard sensory and sighting dominances matched in only 55% of subjects. The Preferential EDS (ranging from −0.7 to +0.9) and MAS-2EV EDS (ranging from −0.6 to +0.4) were highly correlated. Selecting the eye for far in monovision with the MAS-2EV, sensory, or sighting tests would have resulted in 79%, 64%, and 43% success considering the Preferential test as the gold standard.
Conclusions
Tests based on perceptual preference allow selection of the preferred monovision correction and measurement of dominance strength.
Translational Relevance
The binocular visual simulator allows efficient implementation of eye preference tests for monovision in clinical use.